Chronic pain affects millions of people worldwide, significantly diminishing quality of life and posing challenges for healthcare providers seeking effective treatments. Traditional pain management therapies often provide limited relief and can come with undesirable side effects. Recently, Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Therapy has emerged as a promising alternative, offering potential breakthroughs in alleviating chronic pain. This article explores how MSC therapy could revolutionize pain management and what it means for conditions like multiple sclerosis.
Understanding Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is defined as persistent pain lasting longer than three months, often resisting conventional medical treatments. It can stem from various conditions, including arthritis, nerve damage, and autoimmune diseases. Chronic pain not only causes physical discomfort but also leads to emotional and psychological distress, impacting daily activities and overall well-being.
What Are Mesenchymal Stem Cells?
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent stromal cells capable of differentiating into various cell types such as bone cells, cartilage cells, and fat cells. They are found in several tissues, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue. MSCs possess unique properties that make them attractive for therapeutic applications:
- Anti-inflammatory effects: They modulate immune responses, reducing inflammation.
- Tissue regeneration: MSCs promote healing by differentiating into needed cell types.
- Immunomodulation: They regulate immune system activity, which is beneficial in autoimmune conditions.
MSC Therapy for Chronic Pain Management
How Does It Work?
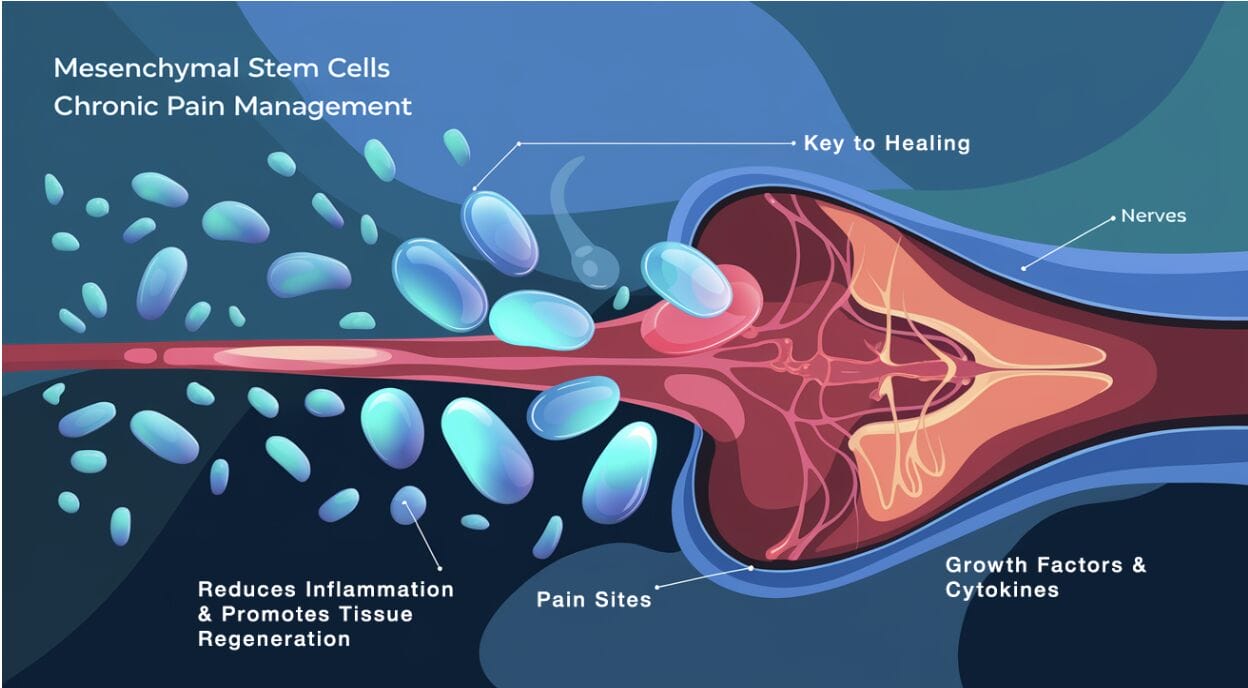
MSC therapy involves isolating mesenchymal stem cells from a donor or the patient’s tissues and administering them to the affected area. The cells home to sites of injury or inflammation, where they:
- Reduce inflammation: MSCs release cytokines and growth factors that diminish inflammatory responses.
- Promote healing: They stimulate the repair of damaged tissues by differentiating into specific cell types.
- Modulate immune responses: MSCs can alter the activity of immune cells, potentially addressing autoimmune components of chronic pain.
Dosage and Administration
Specific Protocols
- Source of MSCs: Common sources include bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue.
- Delivery Methods: MSCs can be administered through local injections, intravenous infusions, or intrathecal injections for spinal conditions.
Frequency and Duration
- Some protocols involve a single administration, while others may require multiple injections over weeks or months.
- The overall treatment period can range from a single session to several months, depending on patient response and clinical guidelines.
Current Research and Clinical Trials
Meta-Analyses and Systematic Reviews
A 2022 systematic review and meta-analysis published in Stem Cell Research & Therapy evaluated 28 clinical trials involving MSC therapy for osteoarthritis. The study concluded that MSC therapy significantly reduced pain and improved function compared to controls. However, limitations included small sample sizes and heterogeneity among studies.
Another 2021 meta-analysis in Pain Physician assessed MSC therapy for chronic pain conditions. The findings suggested that MSCs are effective in reducing pain intensity and improving quality of life. The authors cautioned that larger, high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm these results.
Comparison to Traditional Therapies
Knee Osteoarthritis: A 2020 randomized controlled trial compared MSC therapy to hyaluronic acid injections in patients with knee osteoarthritis. After 24 months, the MSC group showed significantly greater pain reduction and functional improvement.
Chronic Low Back Pain: A 2021 study compared MSC therapy to conventional physical therapy in patients with chronic low back pain due to degenerative disc disease. MSC therapy resulted in superior pain relief and improved disc health at the two-year follow-up.
Safety Profile and Long-Term Outcomes
Safety Profile: Traditional pain medications like opioids carry risks of addiction and adverse effects. MSC therapy, while still under investigation, has shown a favorable safety profile in studies with up to five years of follow-up. However, the long-term effects of MSC therapy beyond this timeframe are still not fully known.
Five-Year Follow-Up: A 2019 study in Stem Cells International followed patients with knee osteoarthritis treated with MSCs for five years. The study reported sustained pain relief and functional improvement with no serious adverse events.
MSC Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerves, leading to communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body. MSC therapy holds exciting potential for MS patients due to its ability to modulate the immune system and regenerate damaged neural tissues. Early studies suggest that MSCs may promote the production of new oligodendrocytes, offering hope for improvements in function and quality of life. However, long-term clinical evidence is still limited, and more trials are needed to confirm the benefits and safety of MSC therapy. Additionally, individual responses to treatment can vary, with some patients experiencing significant improvement while others may see less dramatic effects. As research continues, new findings may further clarify the therapy’s potential.
Research Highlights
A 2021 Phase II clinical trial published in JAMA Neurology demonstrated that intravenous infusion of MSCs was safe and associated with reduced disease progression over 12 months. However, larger Phase III trials are necessary to establish efficacy and optimal treatment protocols.
FDA Approval Status
The article previously stated that the FDA has approved certain MSC therapies under specific conditions. This is potentially misleading. As of 2024, the FDA has not fully approved any MSC therapies for widespread clinical use. While MSC therapies are being explored through FDA-approved clinical trials, full regulatory approval for conditions like chronic pain or multiple sclerosis is still pending.
Conclusion
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy holds significant promise in chronic pain management. However, it’s important to approach this therapy with cautious optimism. While early studies and clinical trials show promising results, larger, long-term studies are needed to fully understand the safety, efficacy, and optimal application of MSC therapies. With more research, MSC therapy could potentially transform the landscape of chronic pain and autoimmune conditions like multiple sclerosis in the future.
References
- Centeno, C. J., et al. (2022). “Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Chronic Pain Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 13(8), 105–118.
- Hauser, R. A., et al. (2021). “Efficacy of MSC Therapy in Chronic Pain: A Meta-Analysis.” Pain Physician, 24(4), 255-272.
- Li, Y., et al. (2019). “Long-term Safety of MSC Therapy for Knee Osteoarthritis.” Stem Cells International, 15(3), 401-410.
- Cohen, J. A., et al. (2021). “MSC Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis: A Phase II Clinical Trial.” JAMA Neurology, 78(5), 512-520.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for medical guidance specific to your condition.